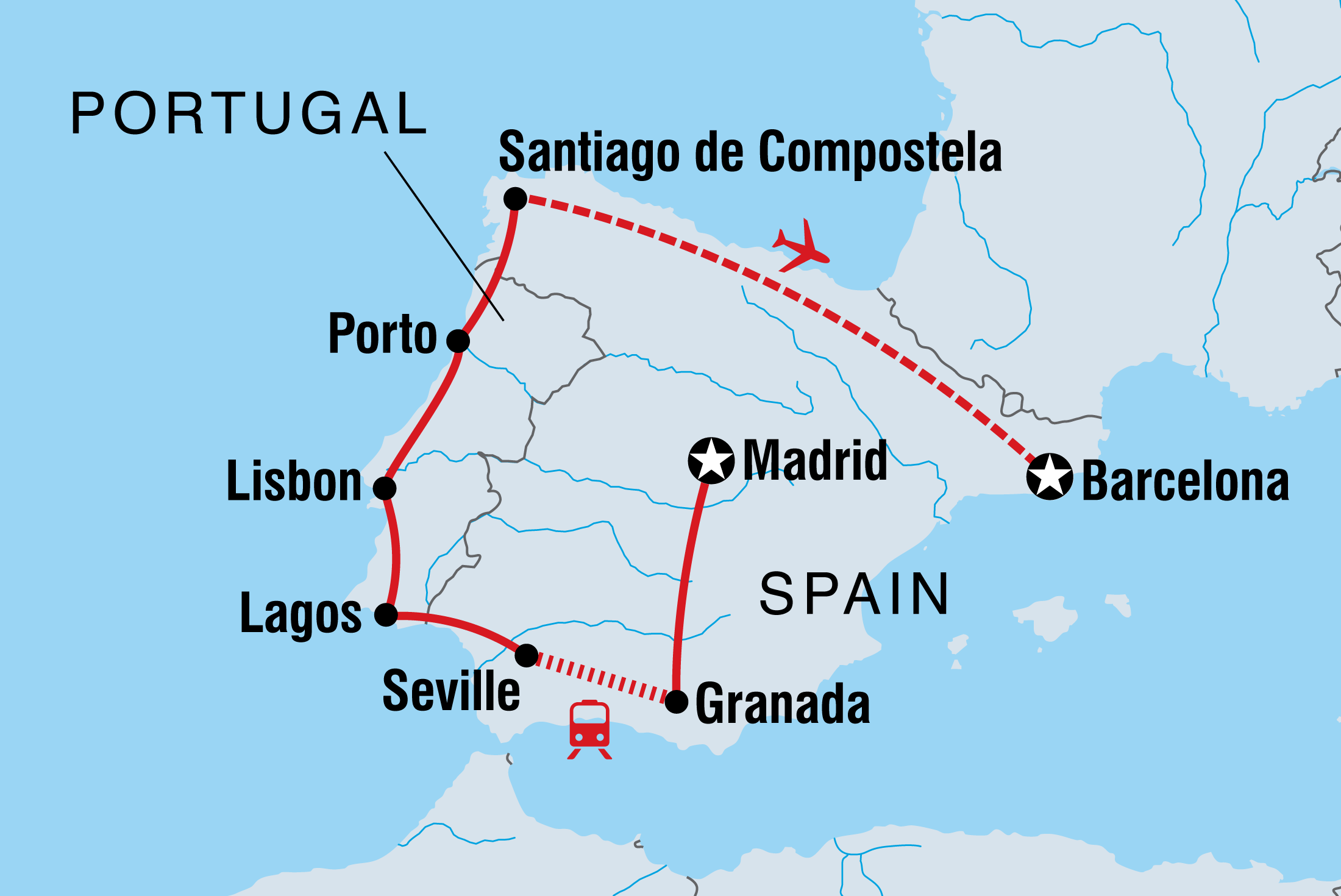
How To Get From Granada To Lisbon
How To Get From Granada To Lisbon. Bus schedule from granada to lisbon showing buses for tomorrow, monday, september 12 alsa 05:00amgranada23h30 04:30amlisbon 0 transfers €83 alsa. Ad choose the best fare and route option from granada to lisbon.
The relationship between a symbol along with the significance of the sign can be known as"the theory of significance. The article we'll be discussing the problems with truth conditional theories of meaning, Grice's study of speaker-meaning, as well as its semantic theory on truth. We will also discuss evidence against Tarski's theories of truth.
Arguments against the truth-based theories of significance
Truth-conditional theories of understanding claim that meaning is a function of the conditions of truth. However, this theory limits understanding to the linguistic processes. The argument of Davidson essentially states that truth-values might not be truthful. So, we need to be able to distinguish between truth-values versus a flat assertion.
The Epistemic Determination Argument is an attempt to establish truth-conditional theories for meaning. It is based upon two basic principles: the completeness of nonlinguistic facts, and knowledge of the truth-condition. But Daniel Cohnitz has argued against these assumptions. Therefore, this argument doesn't have merit.
Another frequent concern with these theories is the lack of a sense of meaning. But this is addressed by mentalist analysis. In this way, the meaning is evaluated in relation to mental representation rather than the intended meaning. For example one person could be able to have different meanings for the identical word when the same person is using the same words in 2 different situations, yet the meanings associated with those terms could be the same if the speaker is using the same word in various contexts.
While the major theories of meaning try to explain the interpretation in ways that are based on mental contents, other theories are often pursued. This may be due to some skepticism about mentalist theories. They also may be pursued from those that believe that mental representation must be examined in terms of linguistic representation.
One of the most prominent advocates of this position The most important defender is Robert Brandom. This philosopher believes that meaning of a sentence is dependent on its social and cultural context, and that speech acts related to sentences are appropriate in the situation in which they are used. So, he's developed a pragmatics concept to explain the meanings of sentences based on the normative social practice and normative status.
Problems with Grice's study of speaker-meaning
Grice's analysis on speaker-meaning places much emphasis on the utterer's intention and the relationship to the meaning that the word conveys. Grice believes that intention is an abstract mental state that needs to be understood in order to determine the meaning of a sentence. But, this argument violates speaker centrism in that it analyzes U-meaning without considering M-intentions. In addition, Grice fails to account for the issue that M intentions are not limitless to one or two.
The analysis also does not take into account some important cases of intuitional communication. For example, in the photograph example of earlier, the individual speaking does not make clear if she was talking about Bob the wife of his. This is a problem as Andy's photo doesn't reveal the fact that Bob as well as his spouse are unfaithful or faithful.
Although Grice believes that speaker-meaning is more fundamental than sentence-meaning, there is some debate to be had. In reality, the distinction is crucial for the naturalistic respectability of non-natural meaning. In reality, the aim of Grice is to present naturalistic explanations that explain such a non-natural meaning.
To appreciate a gesture of communication it is essential to understand the intention of the speaker, and this is an intricate embedding of intents and beliefs. Yet, we do not make sophisticated inferences about mental states in simple exchanges. In the end, Grice's assessment of meaning-of-the-speaker is not in accordance with the psychological processes that are involved in communication.
While Grice's story of speaker-meaning is a plausible description in the context of speaker-meaning, it is not complete. Others, including Bennett, Loar, and Schiffer, have provided more elaborate explanations. However, these explanations have a tendency to reduce the validity to the Gricean theory, because they treat communication as an act that can be rationalized. The basic idea is that audiences believe that a speaker's words are true because they understand the speaker's motives.
Furthermore, it doesn't cover all types of speech acts. Grice's study also fails recognize that speech acts are frequently employed to explain the significance of a sentence. The result is that the concept of a word is reduced to what the speaker is saying about it.
The semantic theory of Tarski's is not working. of truth
Although Tarski claimed that sentences are truth bearers it doesn't mean a sentence must always be accurate. Instead, he attempted to define what constitutes "true" in a specific context. His theory has become an integral part of modern logic and is classified as a deflationary theory, also known as correspondence theory.
One drawback with the theory on truth lies in the fact it cannot be applied to natural languages. This is because of Tarski's undefinabilitytheorem, which says that no bivalent language can have its own true predicate. Even though English might seem to be an one exception to this law but it does not go along with Tarski's stance that natural languages are semantically closed.
But, Tarski leaves many implicit conditions on his theory. For instance the theory should not contain false sentences or instances of the form T. Also, it is necessary to avoid being a victim of the Liar paradox. Another drawback with Tarski's theory is that it's not as logical as the work of traditional philosophers. In addition, it's impossible to explain all instances of truth in the ordinary sense. This is a major problem for any theories of truth.
Another issue is that Tarski's definition of truth is based on notions of set theory and syntax. These aren't appropriate for a discussion of infinite languages. Henkin's method of speaking is well-established, however, it doesn't support Tarski's conception of truth.
In Tarski's view, the definition of truth controversial because it fails recognize the complexity the truth. For instance, truth can't play the role of an axiom in an understanding theory, and Tarski's axioms cannot provide a rational explanation for the meaning of primitives. Furthermore, his definitions of truth does not fit with the notion of truth in theory of meaning.
But, these issues can not stop Tarski from using the truth definition he gives and it does not fall into the'satisfaction' definition. In actual fact, the definition of truth isn't so clear and is dependent on particularities of object language. If you're interested to know more, take a look at Thoralf Skolem's 1919 paper.
There are issues with Grice's interpretation of sentence-meaning
The issues with Grice's analysis regarding the meaning of sentences could be summarized in two key elements. First, the intentions of the speaker must be recognized. Second, the speaker's wording must be accompanied with evidence that proves the intended outcome. But these conditions may not be achieved in every case.
The problem can be addressed with the modification of Grice's method of analyzing sentence interpretation to reflect the meaning of sentences that don't have intention. This analysis also rests on the idea that sentences can be described as complex and are composed of several elements. So, the Gricean analysis isn't able to identify contradictory examples.
This critique is especially problematic when we consider Grice's distinctions between meaning of the speaker and sentence. This distinction is the foundational element of any naturalistically valid account of sentence-meaning. This theory is also vital for the concept of conversational implicature. It was in 1957 that Grice developed a simple theory about meaning that expanded upon in subsequent research papers. The core concept behind significance in Grice's research is to take into account the speaker's motives in determining what message the speaker wants to convey.
Another issue with Grice's approach is that it does not allow for intuitive communication. For instance, in Grice's example, there is no clear understanding of what Andy intends to mean when he claims that Bob is unfaithful with his wife. Yet, there are many examples of intuition-based communication that are not explained by Grice's study.
The main premise of Grice's model is that a speaker's intention must be to provoke an effect in the audience. However, this argument isn't rationally rigorous. Grice sets the cutoff by relying on an individual's cognitive abilities of the partner and on the nature of communication.
Grice's theory of sentence-meaning is not very plausible even though it's a plausible analysis. Other researchers have come up with deeper explanations of meaning, but they are less plausible. Additionally, Grice views communication as a rational activity. Audiences justify their beliefs through recognition of an individual's intention.
Ad choose the best fare and route option from granada to lisbon. Granada to lisbon route planner get the best route from granada to lisbon with viamichelin. The cheapest way to get from backpackers inn, granada to lisbon costs only €2050, and the quickest way takes just 16¼ hours.
Flights From Granada To Lisbon Cover The 318 Miles (513 Km) Long Journey Taking On Average 3 H 35 Min With Our Travel Partners Like Air Nostrum, Vueling Or Iberia.
Ad choose the best fare and route option from granada to lisbon. Choose one of the following options for the granada to lisbon route: Find the travel option that best suits you.
To Travel By Train From Granada In Spain To Lisbon In Portugal, You Have Three Options.
Granada to lisbon route planner get the best route from granada to lisbon with viamichelin. Book flight tickets from granada to lisbon with extra peace of mind. The cheapest way to get from granada to lisbon is by bus, car, train.
Flies To Lisbon From Bristol, Edinburgh, Liverpool, London Gatwick And London Luton.
Compare routes from granada to lisbon below. Return flights can cost £ 70 ( us$ 80). & 00 frequently offer the best deals to lisbon flights, or select your.
Second One In The North.
First one by night train from madrid or irun to lisbon. Choose the best one for you. Find the travel option that best suits you.
Travel From Spain To Portugal Is:.
The direct drive from granada to lisbon is 446 mi (718 km), and should have a drive time of 6 hrs 39 mins in normal traffic. Lisbon 5 miles from central lisbon closest. Don't forget about exploring your own hometown with a staycation.
Post a Comment for "How To Get From Granada To Lisbon"